8 min to read
Virtual Android Emulator Online
The evolution of Android emulators has significantly impacted developers, testers, and the gaming community. These software solutions simulate Android devices on non-native platforms and execution without the necessity for physical hardware. This article presents an in-depth examination of virtual Android emulators, focusing on their architecture, operational methodologies, advantages, constraints, and contemporary industry applications. Top Online Android Emulator Platforms The market for o
The evolution of Android emulators has significantly impacted developers, testers, and the gaming community. These software solutions simulate Android devices on non-native platforms and execution without the necessity for physical hardware.
This article presents an in-depth examination of virtual Android emulators, focusing on their architecture, operational methodologies, advantages, constraints, and contemporary industry applications.
Top Online Android Emulator Platforms
The market for online Android emulators has grown substantially, with several major players offering cloud-based environments that simulate Android devices.
Below, we’ll dive into the most popular and widely used virtual Android emulator platforms, analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, features, and real-world use cases.
1. BrowserStack App Live
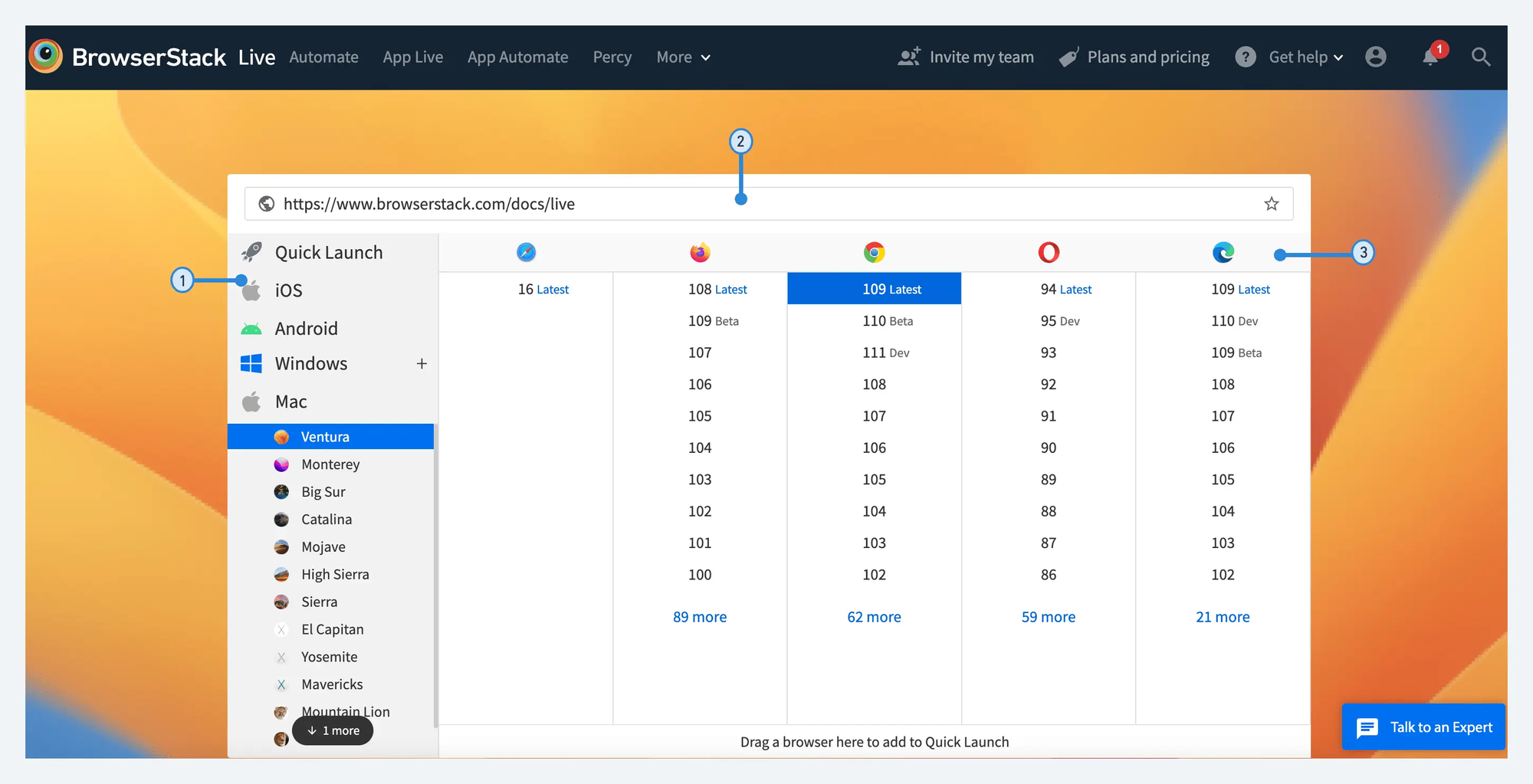
Overview:
BrowserStack is among the most popular cloud testing platforms worldwide. Known for its cross-browser testing tools, BrowserStack also provides powerful App Live and App Automate services that allow developers to test mobile applications on a wide range of real Android (and iOS) devices directly in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Real Android device emulation and live interaction.
- Access to hundreds of physical devices hosted on BrowserStack’s cloud.
- Supports both manual testing and automation (via App Automate).
- Debugging features: inspect logs, capture screenshots, device screen recording.
- Integrations with CI/CD tools (Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions).
- Network simulation for different bandwidths and conditions.
- Customizable device setups (different Android OS versions, screen sizes, manufacturers).
Pros:
- Reliable, accurate, and based on actual devices rather than pure emulators.
- Large device pool for compatibility testing.
- Strong enterprise support with security compliance (GDPR, SOC2).
- Easy integration with development workflows.
Cons:
- Expensive for individuals or small teams.
- Requires constant internet connection — latency may affect usability.
Ideal For:
Enterprise software teams, mobile app developers, and QA testers who require high accuracy across many Android devices.
Pricing:
Subscription-based, starting from ~$39/month for individuals. Enterprise pricing is custom.
2. Appetize.io

Overview:
Appetize.io has carved a niche as a lightweight, browser-based Android emulator that focuses on ease of use and accessibility. It allows immediate streaming of an Android environment inside any browser with no installation required.
Key Features:
- Upload your APK/IPA and run apps in seconds.
- Fully browser-based, works on any device (desktop, tablet, even mobile).
- Embeddable emulator — can be integrated into documentation, websites, or demos.
- API support to automate processes such as launching sessions.
- Screen sharing, remote testing, and debugging tools available.
Pros:
- Super easy to set up (drag and drop APK into browser).
- Ideal for live demos of apps and training sessions.
- Cloud-power reduces need for local system resources.
- Freemium model is attractive for students and small-scale developers.
Cons:
- Limited features compared to more comprehensive platforms like BrowserStack.
- Not ideal for gaming use cases — designed for app demos/testing.
- Session time restrictions on free plans.
Ideal For:
Developers needing quick testing, customer demos, sales pitches, and educational purposes.
Pricing:
Free basic tier with time limits; paid usage starts at $40/month for extended runtime and enterprise integration.
3. Genymotion Cloud

Overview:
Genymotion started as a desktop Android emulator popular among developers, but it has since evolved into Genymotion Cloud, offering Android VMs (virtual machines) that can run on-demand either on Genymotion SaaS cloud or on popular cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
Key Features:
- Wide range of Android versions (from Android 4.1 to the latest).
- Virtual devices hosted in the cloud or deployable on your personal cloud infrastructure.
- Sensor simulation: GPS, accelerometer, battery states, camera.
- Works via browser or ADB connection.
- Multi-instance capability – run several devices at once.
- Ideal for automation testing with frameworks like Appium.
Pros:
- Extremely flexible — can run on public clouds, private clouds, or Genymotion’s own SaaS.
- Scalability: launch hundreds of Android instances simultaneously for massive testing.
- Powerful developer features and integrations.
Cons:
- Interface can be overwhelming for non-technical users.
- Primarily suited for testing — not gaming.
- Costs accumulate quickly on pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Ideal For:
Professional Android developers, QA automation engineers, and enterprises seeking scalable Android test environments.
Pricing:
Starts at $0.05 per minute (pay as you go); enterprise contracts available.
4. LambdaTest

Overview:
LambdaTest is a cloud-based platform traditionally focused on cross-browser testing but, similar to BrowserStack, it also provides mobile app testing support with virtual and real device cloud.
Key Features:
- Online Android emulation across different devices.
- Integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines.
- Parallel testing – run automation tests on multiple devices simultaneously.
- Offers both Android and iOS device testing.
- Debugging options with video recordings, screenshots, and developer logs.
Pros:
- Affordable compared to BrowserStack.
- Excellent automation support (Appium, Espresso).
- 24/7 customer support and active development.
Cons:
- Fewer devices in the pool compared to BrowserStack.
- Performance can vary based on user load.
Ideal For:
Small to mid-level businesses looking for a cost-effective testing platform.
Pricing:
Starts with free trial; paid plans begin around $15–25/month.
5. Sauce Labs

Overview:
Sauce Labs is another leading cloud testing provider focusing heavily on enterprise-scale automated testing. It provides access to Android emulators, iOS simulators, and even thousands of real devices in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based Android emulators for app testing.
- Large device and OS coverage.
- Integrates with leading testing frameworks (Appium, Espresso, XCUITest).
- Strong enterprise-grade analytics.
- Live and automated testing.
Pros:
- Highly scalable, designed for large QA teams.
- Strong testing framework support.
- Excellent analytics, debug options, and collaboration tools.
Cons:
- Expensive for individual developers.
- Has a learning curve — requires some setup.
Ideal For:
Large enterprise teams with complex testing requirements.
Pricing:
Custom pricing, typically enterprise-focused.
6. Other Notable Platforms
In addition to the top five, several smaller or specialized services also provide valuable Android online emulation options:
TestObject (by Sauce Labs)
- A device cloud specifically focused on mobile.
- Offers both online emulators and real devices.
NoxPlayer Cloud (experimental)
- Aimed at gamers, Nox is working on a browser-based version.
- Limited availability as of now.
ApkOnline.net
- Free, web-based emulator focused on running APK files quickly.
- Limited but useful for basic app usage.
Firebase Test Lab (by Google)

- Cloud device testing integrated into Google Firebase ecosystem.
- Excellent for Android developers seeking direct Google ecosystem integration.
Comparison Table of Online Android Emulator Platforms
| Platform | Best For | Pricing Model | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|
| BrowserStack | Enterprise app testing | Subscription | Huge real-device pool |
| Appetize.io | Quick app demos, easy trials | Freemium/Monthly | Browser-embeddable emulators |
| Genymotion Cloud | Scalable developer testing | Pay-as-you-go | Cloud VM integration (AWS, GCP) |
| LambdaTest | Affordable testing for SMBs | Subscription | Budget-friendly with CI/CD support |
| Sauce Labs | Enterprise automation at scale | Custom Enterprise | Large-scale automation + analytics |
| ApkOnline | Casual app use, students | Free | Quick APK testing in browser |
Conceptual Framework: Android Emulation
An Android emulator is a sophisticated software construct that replicates an Android device’s functional parameters on a host system. It establishes a virtualized environment, encapsulating critical elements such as the Android operating system, graphical user interface, and hardware abstraction layers.
This replication enables developers to execute, test, and debug Android applications within a controlled ecosystem, ensuring compatibility across diverse hardware configurations and OS versions.
Fundamental Attributes of Android Emulators
- Hardware and Software Virtualization: Emulates an Android device's CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage with configurable parameters.
- APK Deployment Capabilities: Facilitates direct APK installation for comprehensive testing protocols.
- Mobile Web Compatibility Assessment: Supports responsive design evaluation across browsers such as Chrome and Firefox.
- Integrated Debugging Mechanisms: Incorporates advanced tools, including breakpoint handling and real-time code evaluation.
- Performance Analytics: Enables profiling of CPU and memory utilization to optimize app efficiency.
- Touch and Sensor Emulation: Simulates multi-touch gestures and device sensors for real-world accuracy.
Architectural Framework of Android Emulators
Android emulators employ multiple interdependent subsystems to generate a virtualized Android runtime environment. These subsystems include:
- Emulation Core (QEMU or Equivalent): Facilitates CPU instruction set translation and peripheral hardware abstraction.
- Virtual Machine Management (KVM, HAXM): Ensures isolation and optimized execution of Android instances.
- Graphical Rendering Engine: Renders UI elements in synchronization with host GPU acceleration.
- Network Emulation Layer: Establishes virtualized network interfaces for connectivity testing.
- Debugging and Profiling Suite: Integrated within Android Studio and similar IDEs for seamless debugging workflows.
Advantages of Virtualized Android Environments
For Development and Quality Assurance
- Resource Optimization: Minimizes dependency on a diverse array of physical devices, reducing overhead costs.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility Validation: Ensures functionality across heterogeneous device ecosystems.
- Accelerated Prototyping: Streamlines iterative testing and feature deployment.
For Application Testing and Security Assurance
- Controlled and Reproducible Testing Conditions: Facilitates rigorous assessment of application behavior under predefined constraints.
- Simulation of Real-World Variables: Emulates diverse environmental factors, including network conditions and geolocation inputs.
For Advanced Gaming Integration
- Enhanced User Interface Adaptability: Supports keyboard and controller mapping for improved interactivity.
- Performance Scalability: Leverages high-performance desktop computing for resource-intensive mobile games.
Cloud-Based Android Emulation: Paradigm Shift
Cloud-based emulators redefine Android virtualization by leveraging distributed computing infrastructure. These platforms eliminate local hardware constraints while providing expansive device compatibility.
Distinctive Features
- Web-Based Accessibility: Enables emulator access via browser interfaces without requiring local installation.
- Extensive Device Repository: Offers remote access to a comprehensive range of Android configurations.
- Automated Testing Pipelines: Seamlessly integrates with CI/CD workflows for automated regression testing.
Mobile Testing Resource Hub: here
Android Emulators & iOS Simulators: here"
Key Advantages
- Eliminates On-Premise Resource Dependencies
- Facilitates Remote Collaboration and Scalability
- Optimized for Parallel Testing Scenarios
Comparative Evaluation: Virtual Emulators vs. Physical Devices
| Feature | Physical Devices | Cloud-Based Emulators |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Fidelity | High | Moderate |
| Cost Implications | Significant | Relatively Lower |
| Geographic Accessibility | Restricted | Global Availability |
| Setup Complexity | Extensive | Minimal |
While physical devices remain indispensable for high-fidelity testing, cloud-based emulators offer superior scalability and cost efficiency for iterative development processes.
Constraints and Considerations
Despite their utility, virtualized Android emulators present several challenges:
- Latency and Processing Overheads: Hardware abstraction introduces execution delays relative to native environments.
- Sensor Fidelity Limitations: Emulated sensors may not accurately replicate the nuanced behaviors of physical counterparts.
- Network Dependency: Cloud-based solutions necessitate consistent and high-bandwidth connectivity for optimal performance.
Strategic Applications
Application Engineering and Compatibility Assurance
Virtual emulation facilitates robust cross-platform compatibility testing, ensuring seamless user experiences across diverse Android ecosystems.
Security and Penetration Testing
Cloud-based Android environments enable controlled security testing, allowing researchers to identify vulnerabilities under isolated conditions.
Game Optimization and Performance Benchmarking
Gaming applications benefit from virtualized environments through enhanced scalability, enabling refined performance analysis.
Final Thoughts on Emulator Platforms
The choice of virtual Android emulator online depends heavily on the user’s goals and scale.
- For individuals & small-scale testing: Appetize.io and ApkOnline work well.
- For developers needing flexibility: Genymotion Cloud is a top option.
- For enterprises: BrowserStack and Sauce Labs are the strongest players.
- For cost-conscious teams: LambdaTest offers feature-rich plans at a lower price point.
These platforms, while distinct, share one thing in common — they bring Android to the cloud, reducing the need for physical devices and enabling faster, more scalable app development workflows.
References
🚀 Try Codersera Free for 7 Days
Connect with top remote developers instantly. No commitment, no risk.
Tags
Trending Blogs
Discover our most popular articles and guides
10 Best Emulators Without VT and Graphics Card: A Complete Guide for Low-End PCs
Running Android emulators on low-end PCs—especially those without Virtualization Technology (VT) or a dedicated graphics card—can be a challenge. Many popular emulators rely on hardware acceleration and virtualization to deliver smooth performance.
Android Emulator Online Browser Free
The demand for Android emulation has soared as users and developers seek flexible ways to run Android apps and games without a physical device. Online Android emulators, accessible directly through a web browser.
Free iPhone Emulators Online: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the best free iPhone emulators that work online without downloads. Test iOS apps and games directly in your browser.
10 Best Android Emulators for PC Without Virtualization Technology (VT)
Top Android emulators optimized for gaming performance. Run mobile games smoothly on PC with these powerful emulators.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.
ApkOnline: The Android Online Emulator
ApkOnline is a cloud-based Android emulator that allows users to run Android apps and APK files directly from their web browsers, eliminating the need for physical devices or complex software installations.
Best Free Online Android Emulators
Choosing the right Android emulator can transform your experience—whether you're a gamer, developer, or just want to run your favorite mobile apps on a bigger screen.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.