10 min to read
SQL Vs NoSQL: Which One Is The Best For You?
Structured Query language (SQL) SQL database is a domain-specific programming language used for managing, and designing data stored in a relational database management system (RDBMS). Also, it is used for stream processing in RDBMS. Relational databases use relations (typically called tables) to store data and match that particular data by using common characteristics within that dataset. Here’s A Beginner’s Guide To SQL for you to go through! SQL often pronounced as “S-Q-L” or “See-Quel” is
Structured Query language (SQL)
SQL database is a domain-specific programming language used for managing, and designing data stored in a relational database management system (RDBMS). Also, it is used for stream processing in RDBMS. Relational databases use relations (typically called tables) to store data and match that particular data by using common characteristics within that dataset.
Here’s A Beginner’s Guide To SQL for you to go through!
SQL often pronounced as “S-Q-L” or “See-Quel” is the standard language for dealing with Relational Databases invented in 1974 and is still going strong with their latest released version in 2016. It is particularly useful in handling structured data which is data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
A relational database defines relationships in the form of tables and SQL is effectively used to insert, search, update, delete database records.

Database
SQL database is originally based on Relational Algebra and Tuple relational calculus consisting of various types of statements. These statements can also be classified as sublanguages, called: A Data query language (DQL), Data Definition Language (DDL), a Data Control Language (DCL), and a Data Manipulation Language (DML).
Schema For SQL
A Schema in SQL is a template/pattern that describes qualities regarding the information a database will store.
Specifically, it describes:
- Type – Type of information refers to a specific piece of information and general attributes of that particular information. For example, integers can be positive or negative and they don’t have a fractional part. This piece of information about their characteristics makes a huge difference in the way they are being efficiently stored.
- Size – The size of each piece of information determines how much space it will occupy in the database. Although the price of storage has come down, still it is not practical to leave an infinite storage space. This information is recognized at the designing stage when the building and maintenance of databases happen.
- Organization – It refers to how the information is grouped and stored as per the user’s convenience and intended use at a particular point in time. Organization of information is stored in such a way that it is on a priority basis and unused or to be used later information is stored separately, making it a comfortable experience for the user.
SQL provides an organized and systematic approach to accessing information through various methods:
- Data query
- Data manipulations (insert, update, and delete),
- Data definition (schema creation and modification),
- Data access control
Although the SQL database is essentially a declarative language, it includes procedural elements also.
Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a system, network, or process, to handle a growing amount of work in an efficient manner or its ability to be enlarged to accommodate that growth. In other words, we can say that a system can optimize its performance level as per the requirement of the system at that stage.
Examples
A few examples of relational databases using SQL are:
- MySQL
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Sybase
- Ingres
- Access
- Postgres
Model:
ACID is a concept that is generally used by database professionals for the evaluation of databases and application architectures in the SQL database model to ensure that data is stored in a safe, consistent, and robust manner
Here, ACID stands for-
A- Atomicity -Atomicity is an all-or-none proposition. During such transactions between two pieces of information either all is saved or none is saved.
C- Consistency The data saved can’t violate any of the database’s integrity. Interrupted changes are rolled back to ensure the database is placed in a state before the change.
I- Isolation – The transaction does not get affected by any other transactions which are happening at other places, this avoids “mid-air collisions.”
D- Durability– Once the transaction happens, any failure or system restart returns the data in an absolutely correct form. Regardless of subsequent system failure, its state remains unaffected.
For a reliable database, all these four attributes should be achieved.
Usage: Which jobs use SQL?
SQL statements are used to perform tasks such as updating and retrieval of data on a database.
A job is a specified series of operations that are sequentially performed by SQL Server Agent. A job performs a wide range of activities, including running Transact- SQL scripts, Command prompt applications, Microsoft ActiveX scripts, Integration Services packages, Analysis Services commands, queries, or Replication tasks.
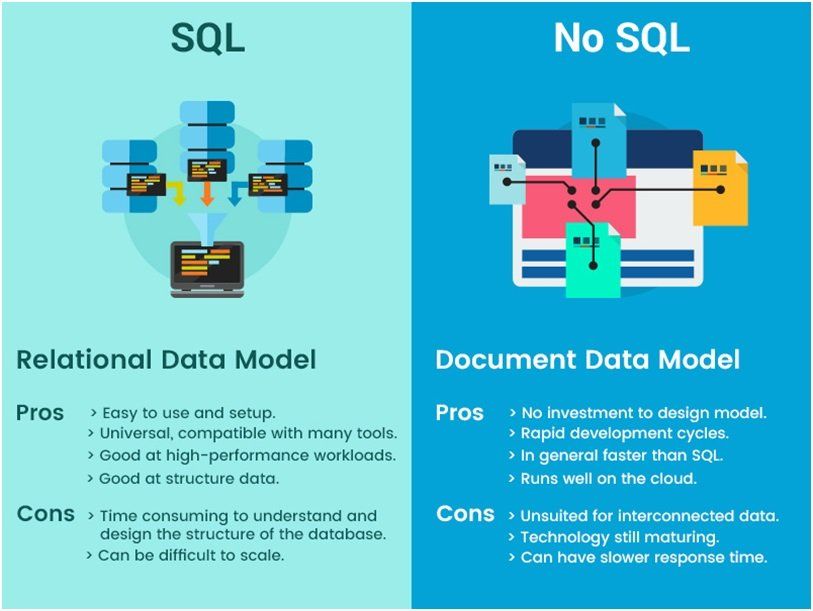
Pros
- High speed– Using SQL queries, the user can quickly and efficiently retrieve a larger amount of data from a database.
- No coding needed– In standard SQL, it is very easy to manage the database without any substantial coding requirements.
- Well-defined standards– Long-established ISO and ANSI standards are strictly followed.
- Portability– It offers great ease to use on PCs, laptops, servers, and even some mobile phones.
Interactive language SQL is used to communicate with greater ease in answering complex queries in a database.
Cons
Along with some benefits, the SQL database comes with certain limitations/ disadvantages:
- Difficult Interface– SQL has a complex interface making it difficult for users to access it.
- Partial Control– Users don’t get full control over the database because of the hidden business rules.
- Implementation– Some of the databases go to the proprietary extensions to standard SQL for ensuring vendor lock-in.
- Cost– The operating cost of a few SQL versions makes it difficult for users to use it.
The average salary of SQL Developer:-
The average annual salary for any SQL developer in the USA is $84,328.
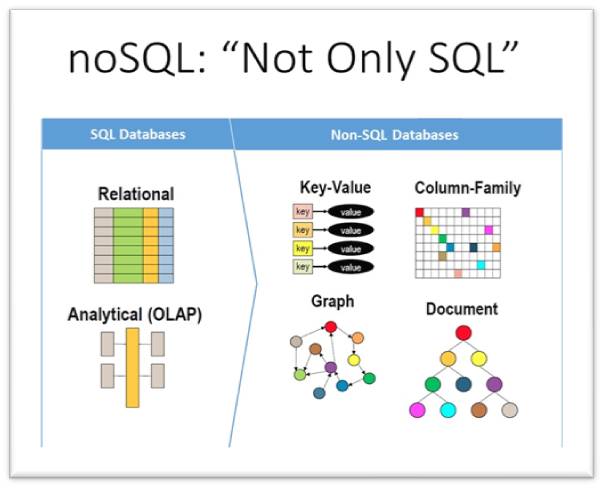
No SQL
NoSQL is a non-relational database management system, that does not require a fixed schema, avoids joins, and is easy to scale. NoSQL database is used for distributed data stores with humongous data storage needs.
NoSQL stands for “not only SQL,” or “Not SQL” an alternative to traditional relational databases where data is placed in tables and schema is carefully designed before the database is built.
A NoSQL database is self-describing, so it does not require a schema. Also, it does not enforce relations between tables in all cases. All its documents are JSON documents, which are complete entities that one can readily read and understand.
A NoSQL database system encompasses a wide range of database technologies that can store structured, semi-structured, unstructured and polymorphic data.
‘NoSQL’ refers to high-performance, non-relational databases that utilize a wide variety of data models. These databases are highly recognized for their ease of use, scalable performance, strong resilience, and wide availability.
Database
According to Wikipedia “A NoSQL database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.”
NoSql is a cloud-friendly approach to employ for your applications.
Schema For NoSql
The formal definition of a database schema is a set of formulas or sentences called “Integrity constraints” imposed on a database.
The term “schema” refers to the organization of data as a blueprint of how the database is constructed, construction here refers to the division of database tables in the case of relational databases.
Scalability
NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable, which means they can handle increased traffic needs immediately, simply by adding more servers to the database. ‘NoSQL’ databases can become larger and more powerful, making them a preferred choice for larger or constantly evolving data sets.

Examples
Presenting here a list of the top 4 NoSQL Databases with their uses:
Model
NoSQL relies upon a softer model known as the BASE model. Here BASE stands for (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency).
Available: Guarantees the availability of the data.
Usage
NoSQL is used for Big data and real-time web apps.
Pros
No SQL provides ease in availability with rich query language and easy scalability. The following are the main advantages of NoSQL databases.
- Elastic scaling
RDBMS might not scale out easily for commodity clusters, but the new versions of the “NoSQL database” are designed to expand transparently to take benefits from new nodes.
- Big data
To combat the growing needs of the volumes of data that are being stored, RDBMS capacity has been increased to match these massive volumes. But with transaction rates, constraints of data volumes that can be practically managed by a single RDBMS are getting difficult to handle by organizations/ enterprises worldwide. NoSql systems provide a solution to all this by handling bigger data needs as displayed in Hadoop.
Cons
Every database has certain advantages and some disadvantages as well, listing here a few of the major NoSql limitations:
- Less Community Support
- Standardization
- Interfaces and Interoperability
Average Salary Of NoSql Developer:-
The average annual salary for a NoSql developer in the USA is $72,174.
Major Differences To Understand in SQL and NoSql Database As Per Business Needs
To understand which is the best data management system between Sql Vs NoSql databases for your organization, we must identify the needs of our business and then make an informed decision. In database technology, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, so it is recommended to analyze SQL Vs NoSql and then decide.
Many businesses rely on both relational and nonrelational databases for different tasks, as NoSQL databases win in speed, safety, cost, and scalability, whereas the SQL database is preferred when the highly structured database is required.
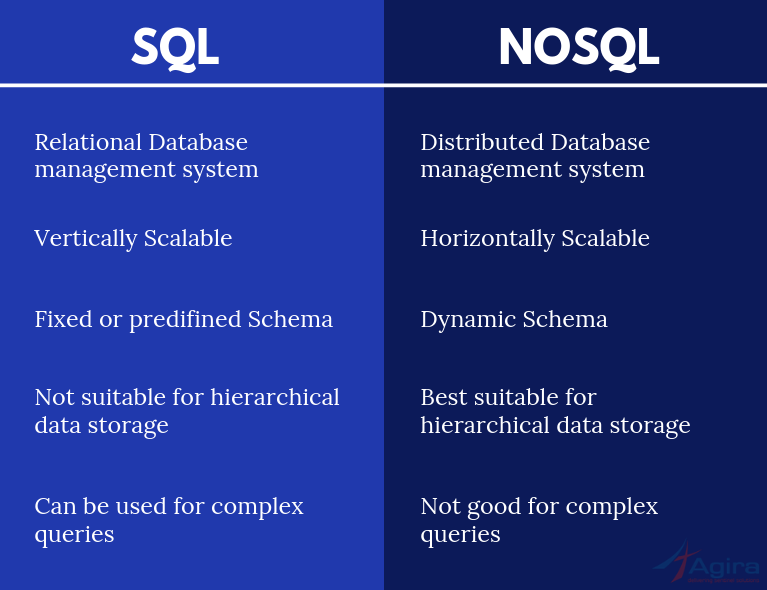
One of the key differentiators is that NoSQL is a column-oriented, non-relational distributed database whereas RDBMS is a row-oriented relational database. Also, they are differentiated based on built, the type of information they store, and how they store
Relational databases are structured, like phone books and Non-relational databases are document-oriented, and distributed, like file folders that store everything from a person’s address and phone number to their Facebook and online shopping preferences, etc.
The major point of differences in SQL Vs NoSql databases are:
- Language– One of the major differences between the SQL database and NoSQL databases is the language. SQL databases use Structured Query Language for defining and manipulating data, making it a widely-used and extremely versatile database. But, it makes it a restrictive language also. SQL requires ‘predefined schemas’ to determine the structure of the data before the user starts working with it. A ‘NoSQL database’ requires a dynamic schema for unstructured data and the data is stored in many different ways, whether it is graph-based, document-oriented, column-oriented, or organized as a KeyValue store. This extreme flexibility in the ‘NoSql database’ allows the user to create documents without having to carefully plan and define their structure. It gives the flexibility to add fields as you go and vary the syntax from one database to another. It also provides the freedom to give each document its unique structure.
- Scalability– Another big difference between SQL and NoSQL is their scalability. In most SQL databases, they are vertically scalable, which means that you can increase the load on a single server by increasing components like RAM, SSD, or CPU. In contrast, NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable, which means that they can handle increased traffic simply by adding more servers to the database. NoSQL databases can become larger and much more powerful, making them the preferred choice for large or constantly evolving data sets.
3. Community– Because of SQL’s advanced and mature useful features in database management, it has a much stronger, huge, and more developed community as compared to ‘NoSQL’. Although NoSQL is growing rapidly its community is not big enough and well-defined in comparison to SQL, because it’s relatively new.
4. Structure– Finally in SQL vs NoSQL differences, an important difference in their structures. SQL databases are table-based and considered a good option for multi-row transactions like in accounting systems or legacy systems that are built on relational structure. NoSQL databases are key-value pairs, wide-column stores, graph databases, or document-based in structure
List Of Top Companies Using SQL:
- Hootsuite
- Gauges
- CircleCI
List Of Top Companies Using NoSQL:
- Uber
- Airbnb
- Kickstarter
Conclusion:
One of the most important decisions for your business is what database to go for as per the requirement. Many times it so happens that businesses require both databases at various stages of an application. The onus is on the developer to recognize the right database for a certain application and deploy it as per the need based on query and scalability needs.
- SQL databases are suitable for transactional data where structural change is not required frequently or does not happen at all. Also, data integrity and durability are of paramount importance. Additionally, it is found useful for faster analytical queries.
- NoSQL databases provide better flexibility and scalability yielding high performance with high availability. Also, it is better for big data and real-time web applications.
FAQ's
Which is better SQL or NoSQL?
SQL databases provide great benefits for transactional data whose structure doesn't change frequently (or at all) and where data integrity is paramount. It's also best for fast analytical queries. NoSQL databases provide much more flexibility and scalability, which lends itself to rapid development and iteration.
Is MongoDB a SQL or NoSQL?
Yes, MongoDB is a NoSQL Database. … MongoDB is a document-based database. MongoDB is one of the leading NoSQL databases. NoSQL database is a type of non-relational database, and it is capable of processing structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Is SQL or NoSQL faster?
As for speed, NoSQL is generally faster than SQL, especially for key-value storage in our experiment; On the other hand, NoSQL databases may not fully support ACID transactions, which may result in data inconsistency.
🚀 Try Codersera Free for 7 Days
Connect with top remote developers instantly. No commitment, no risk.
Tags
Trending Blogs
Discover our most popular articles and guides
10 Best Emulators Without VT and Graphics Card: A Complete Guide for Low-End PCs
Running Android emulators on low-end PCs—especially those without Virtualization Technology (VT) or a dedicated graphics card—can be a challenge. Many popular emulators rely on hardware acceleration and virtualization to deliver smooth performance.
Android Emulator Online Browser Free
The demand for Android emulation has soared as users and developers seek flexible ways to run Android apps and games without a physical device. Online Android emulators, accessible directly through a web browser.
Free iPhone Emulators Online: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the best free iPhone emulators that work online without downloads. Test iOS apps and games directly in your browser.
10 Best Android Emulators for PC Without Virtualization Technology (VT)
Top Android emulators optimized for gaming performance. Run mobile games smoothly on PC with these powerful emulators.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.
ApkOnline: The Android Online Emulator
ApkOnline is a cloud-based Android emulator that allows users to run Android apps and APK files directly from their web browsers, eliminating the need for physical devices or complex software installations.
Best Free Online Android Emulators
Choosing the right Android emulator can transform your experience—whether you're a gamer, developer, or just want to run your favorite mobile apps on a bigger screen.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.