3 min to read
React OnClick Event Handling
Events can be handled in React quite similar to the way we do in HTML, these events are click, change, mouseover, etc. But ‘React events’ are written in camelCase syntax. For example “onClick” instead of “onclick” and the function which this event point to would be written in curly braces, for example, onClick={function}. In this blog, we will talk only about ‘onClick‘ event handling. The onClick handler allows you to call a function and perform an action when an element is clicked. Let’s lea
Events can be handled in React quite similar to the way we do in HTML, these events are click, change, mouseover, etc. But ‘React events’ are written in camelCase syntax.
For example “onClick” instead of “onclick” and the function which this event point to would be written in curly braces, for example, onClick={function}.
In this blog, we will talk only about ‘onClick‘ event handling. The onClick handler allows you to call a function and perform an action when an element is clicked.
Let’s learn about this with an example–
Create a new project by the following command:
npm create-react-app reactOnClickwhere reactOnClick is the project name.
Now, go to the project directory and start it-
cdreactOnClicknpm startYou should have your project started in the local host.
Now, in src/App.js, add the following code:
import React from 'react';
function App() {
const testClick = () => {
alert('Hey, you just clicked me');
};
return ( <
div className = "App" >
<
button onClick = {
testClick
} >
Click me!
<
/button> <
/div>
);
}
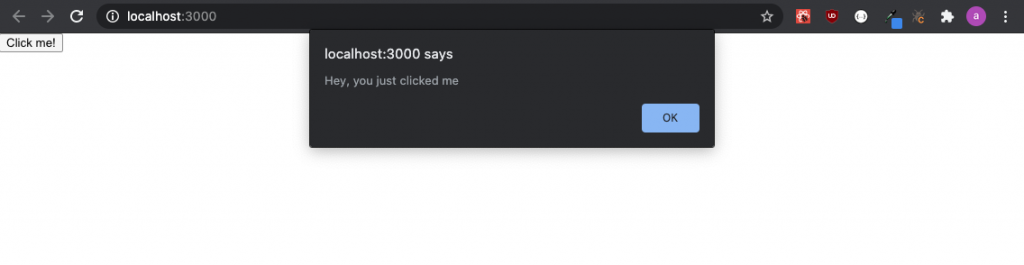
export default App;In this, we have a button that when clicked calls the function “test click”, which alerts the user that he clicked the button.
You will see something like the following after clicking the button–
Some common mistake people do is that they pass the function to the handler with parentheses like:
<button onClick={testClick()}>what it would do is, call the “testClick” function on every render without even clicking it.
It is not necessary to call a function with a name, we can also call inline functions just like:
<button onClick={() => alert('Hey, you just clicked me')}>So now you must be thinking, if we cannot pass the function name with parentheses then how can we pass arguments to a function?
It can be easily done with an inline function calling that function.
To be more clear, see the following code:
function App() {
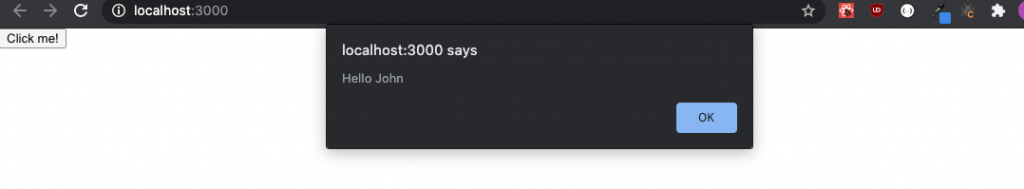
const testClick = (name) => {
alert('Hello ' + name);
};
return ( <
div className = "App" >
<
button onClick = {
() => testClick('John')
} >
Click me!
<
/button> <
/div>
);
}You will see the following in your browser:
Similarly, the states can be managed by ‘onClick’ events-
import React, {
useState
} from 'react';
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return ( <
div className = "App" >
<
h1 > Button is clicked {
count
}
times < /h1> <
button onClick = {
() => setCount(prevState =>
prevState + 1)
} >
Click me!
<
/button> <
/div>
};
}
export default App;And in the browser, we have-

So, Event handlers determine what action should be taken when an event occurs. The “onClick” event is used to listen for click events “onDOM” elements.
Hope you all have a clear picture about ‘onClick’ event handling. Will be sharing more such concepts in my future posts.
FAQ
Q1. How onClick works in React
Ans- The React onClick event handler enables you to call a function and trigger an action when a user clicks an element, such as a button, in your app.
Q2. How do you trigger a click event without clicking React?
Ans- change:
- <button type="button" onClick={this. myFunction(argument)}> myButton </button>
- to this:
- <button type="button" onClick={this. myFunction. bind(this, argument)}> myButton </button>
Q3. What is a preventDefault() in React?
Ans- The preventDefault() method cancels the event if it is cancelable, meaning that the default action that belongs to the event will not occur. For example, this can be useful when: Clicking on a "Submit" button, prevent it from submitting a form.
🚀 Try Codersera Free for 7 Days
Connect with top remote developers instantly. No commitment, no risk.
Tags
Trending Blogs
Discover our most popular articles and guides
10 Best Emulators Without VT and Graphics Card: A Complete Guide for Low-End PCs
Running Android emulators on low-end PCs—especially those without Virtualization Technology (VT) or a dedicated graphics card—can be a challenge. Many popular emulators rely on hardware acceleration and virtualization to deliver smooth performance.
Android Emulator Online Browser Free
The demand for Android emulation has soared as users and developers seek flexible ways to run Android apps and games without a physical device. Online Android emulators, accessible directly through a web browser.
Free iPhone Emulators Online: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the best free iPhone emulators that work online without downloads. Test iOS apps and games directly in your browser.
10 Best Android Emulators for PC Without Virtualization Technology (VT)
Top Android emulators optimized for gaming performance. Run mobile games smoothly on PC with these powerful emulators.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.
ApkOnline: The Android Online Emulator
ApkOnline is a cloud-based Android emulator that allows users to run Android apps and APK files directly from their web browsers, eliminating the need for physical devices or complex software installations.
Best Free Online Android Emulators
Choosing the right Android emulator can transform your experience—whether you're a gamer, developer, or just want to run your favorite mobile apps on a bigger screen.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.