5 min to read
Advantages and Disadvantages of M-Commerce
Mobile commerce, or m-commerce for short, is when you make a purchase using your mobile device. It's a cool evolution of e-commerce that lets Android users buy and sell products and services from just about anywhere, as long as they have a smartphone or tablet. What is M-Commerce? M-Commerce, deals with buying and selling of goods and services through smartphones, tablets etc using digital transactions. It doesn’t require physical contact between two people for sending or receiving the money
Mobile commerce, or m-commerce for short, is when you make a purchase using your mobile device. It's a cool evolution of e-commerce that lets Android users buy and sell products and services from just about anywhere, as long as they have a smartphone or tablet.
What is M-Commerce?
M-Commerce, deals with buying and selling of goods and services through smartphones, tablets etc using digital transactions. It doesn’t require physical contact between two people for sending or receiving the money.
Advantages or Pros of M-Commerce
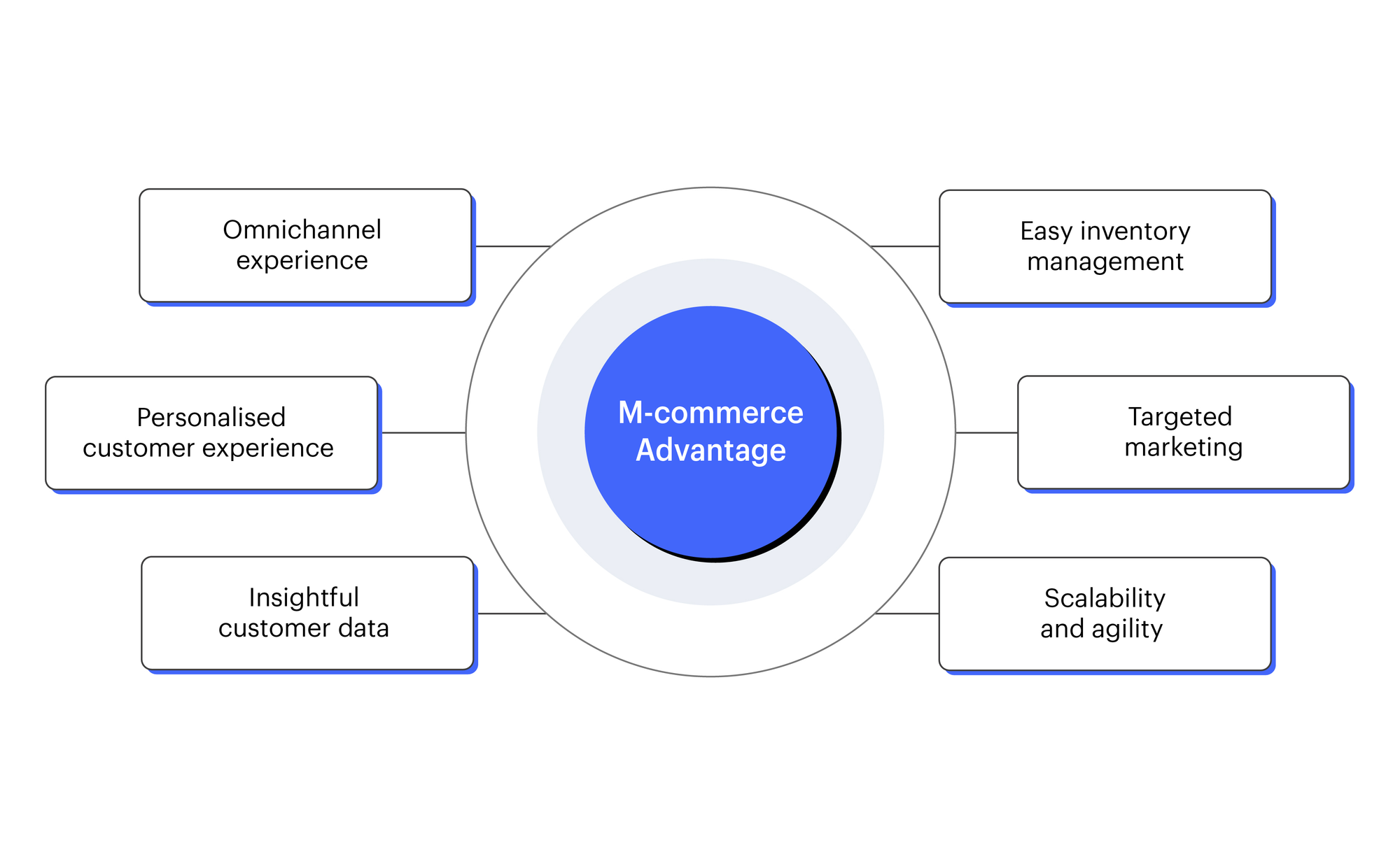
- Convenience:
- Users can shop, pay bills, or access services anytime and anywhere using their mobile devices.
- Eliminates the need to visit physical stores or use desktop computers.
- Wider Reach:
- Businesses can reach a global audience, as mobile devices are widely used across the world.
- Enables access to customers in remote or underserved areas.
- Personalization:
- Mobile apps and websites can use data analytics and AI to offer personalized recommendations and tailored experiences.
- Enhances customer satisfaction and increases sales.
- Faster Transactions:
- Mobile payments (e.g., digital wallets, QR codes) are quicker than traditional payment methods.
- One-click purchasing and autofill features streamline the checkout process.
- Cost-Effective for Businesses:
- Reduces overhead costs associated with maintaining physical stores.
- Mobile marketing (e.g., push notifications, SMS) is often cheaper than traditional advertising.
- Improved Customer Engagement:
- Push notifications and in-app messages help businesses stay connected with customers.
- Features like loyalty programs and gamification increase customer retention.
- Real-Time Access:
- Users can access real-time information, such as product availability, delivery tracking, and stock updates.
- Enhances transparency and trust.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies:
- M-commerce integrates with technologies like AR (augmented reality), AI, and IoT (Internet of Things) to create innovative shopping experiences.
- Examples: Virtual try-ons, voice-activated shopping, and smart home integration.
- Social Commerce:
- Platforms like Instagram and TikTok enable businesses to sell directly through social media, reaching younger, tech-savvy audiences.
- Eco-Friendly Options:
- Digital receipts and mobile tickets reduce paper waste.
- Encourages sustainable shopping practices.
Disadvantages or Cons of M-Commerce

- Security Concerns:
- Mobile devices are vulnerable to hacking, malware, and data breaches.
- Users may hesitate to share sensitive information (e.g., credit card details) due to security risks.
- Limited Screen Size:
- Smaller screens can make it difficult to display detailed product information or provide a seamless browsing experience.
- May lead to a higher rate of cart abandonment.
- Connectivity Issues:
- M-commerce relies on internet connectivity, which can be inconsistent in some areas.
- Poor network speeds can frustrate users and lead to lost sales.
- Battery Life and Device Limitations:
- Mobile devices have limited battery life, which can interrupt shopping sessions.
- Older devices may not support the latest apps or features, limiting accessibility.
- User Experience Challenges:
- Complex navigation or poorly designed apps can frustrate users and drive them away.
- Ensuring a consistent experience across different devices and operating systems can be challenging.
- Privacy Concerns:
- Mobile apps often collect user data, raising concerns about privacy and data misuse.
- Strict regulations (e.g., GDPR) require businesses to handle data responsibly, adding complexity.
- High Development and Maintenance Costs:
- Developing and maintaining a mobile app or responsive website can be expensive.
- Regular updates are required to fix bugs, improve security, and add new features.
- Competition:
- The m-commerce market is highly competitive, making it difficult for smaller businesses to stand out.
- Large players like Amazon and Alibaba dominate the space, creating challenges for new entrants.
- Cart Abandonment:
- Mobile users are more likely to abandon their carts due to distractions or a complicated checkout process.
- Requires strategies like retargeting and simplified checkout to mitigate this issue.
- Dependence on Third-Party Platforms:
- Businesses relying on app stores (e.g., Apple App Store, Google Play) must comply with their policies and pay fees.
- Initial cost of M-commerce begin a business is high.
- Changes in algorithms or policies can impact visibility and sales.
- Cultural and Regional Barriers:
- Different regions have varying levels of mobile adoption, payment preferences, and internet infrastructure.
- Businesses must adapt their strategies to local markets, which can be resource-intensive.
- Fraud and Scams:
- M-commerce platforms are often targeted by fraudsters using fake apps, phishing, or counterfeit products.
- Businesses must invest in robust fraud detection systems.
How does Mobile Commerce work?
M-commerce can be categorised by function as either mobile shopping, mobile banking, or mobile payments. A subcategory of mobile shopping is app commerce, which is a transaction that takes place over a native app.
1. Mobile Applications and Websites:
- Businesses create mobile-friendly websites or dedicated apps that allow users to browse products or services.
- These platforms offer a seamless shopping experience with features like product search, recommendations, reviews etc.
2. User Authentication:
- Users typically register by creating an account or logging in via social media or email.
- Security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA) are used to protect user data.
3. Product Selection and Cart Management:
- Customers select products and add them to their shopping cart.
- They can modify quantities, apply discount codes, review their selections etc before purchase.
4. Payment Processing:
- Mobile commerce supports multiple payment options such as:
- Credit/debit cards
- Digital wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay, PayPal)
- Mobile banking
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services
- Secure encryption and tokenisation technologies protect payment information.
5. Order Fulfillment and Tracking:
- Once payment is confirmed, the business processes the order and ships the product.
- Customers receive order tracking updates via SMS, email, or app notifications.
6. Mobile Payment Technologies:
- Various technologies facilitate mobile payments, including:
- Near Field Communication (NFC): Contactless payments.
- QR Codes: Scan to pay.
- Mobile Point of Sale (mPOS): Businesses use smartphones or tablets to accept payments.
7. Security Measures:
- Mobile commerce platforms implement encryption, biometric authentication (fingerprint, face recognition), and fraud detection to ensure secure transactions.
8. Customer Support:
- Many mobile commerce platforms offer chatbots, live chat, and customer service features for inquiries and returns
In a Nutshell
M-commerce is transforming industries by making transactions faster, more convenient, and accessible. As mobile technology continues to evolve, its applications will expand further, creating new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.
🚀 Try Codersera Free for 7 Days
Connect with top remote developers instantly. No commitment, no risk.
Tags
Trending Blogs
Discover our most popular articles and guides
10 Best Emulators Without VT and Graphics Card: A Complete Guide for Low-End PCs
Running Android emulators on low-end PCs—especially those without Virtualization Technology (VT) or a dedicated graphics card—can be a challenge. Many popular emulators rely on hardware acceleration and virtualization to deliver smooth performance.
Android Emulator Online Browser Free
The demand for Android emulation has soared as users and developers seek flexible ways to run Android apps and games without a physical device. Online Android emulators, accessible directly through a web browser.
Free iPhone Emulators Online: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the best free iPhone emulators that work online without downloads. Test iOS apps and games directly in your browser.
10 Best Android Emulators for PC Without Virtualization Technology (VT)
Top Android emulators optimized for gaming performance. Run mobile games smoothly on PC with these powerful emulators.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.
ApkOnline: The Android Online Emulator
ApkOnline is a cloud-based Android emulator that allows users to run Android apps and APK files directly from their web browsers, eliminating the need for physical devices or complex software installations.
Best Free Online Android Emulators
Choosing the right Android emulator can transform your experience—whether you're a gamer, developer, or just want to run your favorite mobile apps on a bigger screen.
Gemma 3 vs Qwen 3: In-Depth Comparison of Two Leading Open-Source LLMs
The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has brought forth a new generation of open-source AI models that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile than ever.